Nutritional Profile of Kiwi Berries

Kiwi berry nutrition facts – Kiwi berries, also known as mini kiwis, are small, jewel-toned fruits packed with nutrients. Often overlooked in favor of their larger cousins, these bite-sized wonders offer a surprisingly potent nutritional punch, making them a worthy addition to a healthy diet. Their sweet-tart flavor and convenient size make them perfect for snacking or adding to various dishes.
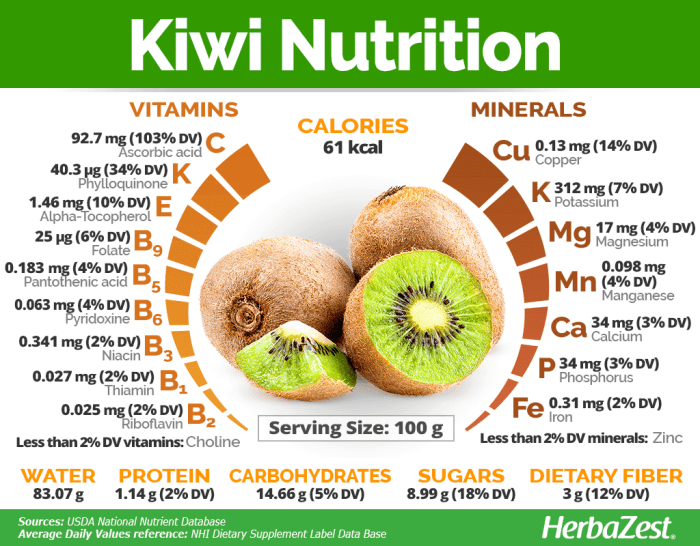
Kiwi Berry Nutritional Breakdown
The following table provides a comprehensive overview of the nutritional content of a typical serving of kiwi berries (approximately 1 cup, or about 150 grams):
| Name | Amount | Unit | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 90 | kcal | ~4% |
| Carbohydrates | 23 | g | ~8% |
| Fiber | 6 | g | ~24% |
| Sugars | 10 | g | ~ |
| Protein | 2 | g | ~4% |
| Fat | 0.5 | g | ~1% |
| Vitamin C | 154 | mg | ~171% |
| Vitamin K | 33 | mcg | ~28% |
| Potassium | 250 | mg | ~7% |
| Manganese | 0.2 | mg | ~10% |
*Note: Daily values are based on a 2000 calorie diet. Actual percentages may vary depending on individual needs and dietary requirements.*
Kiwi berries offer a potent dose of Vitamin C and fiber, making them a nutritional powerhouse. However, a comparison to the purported benefits of jocko go drink nutrition facts reveals a different nutritional profile altogether, highlighting the varying nutrient densities found in different functional foods. Ultimately, the choice between these options depends on individual dietary needs and goals, but the kiwi berry’s readily available nutrients remain a compelling factor.
Antioxidant Content and Health Benefits
Kiwi berries are rich in antioxidants, compounds that protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants contribute to various potential health benefits. Notable antioxidants in kiwi berries include Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and various flavonoids. Vitamin C, in particular, is a potent antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. The flavonoids, such as quercetin, possess anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to cardiovascular health.
The high antioxidant content in kiwi berries contributes to their potential role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases. For example, studies have shown that diets rich in antioxidants are associated with a lower risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer.
Kiwi Berry Nutritional Profile Compared to Other Berries
While blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are also excellent sources of antioxidants and vitamins, kiwi berries stand out in terms of their Vitamin C content. Kiwi berries typically boast significantly higher levels of Vitamin C than blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries. While other berries excel in other areas, such as anthocyanin content (responsible for the vibrant colors), kiwi berries provide a compelling nutritional profile with a notable focus on Vitamin C and fiber.
The specific nutritional composition varies slightly depending on growing conditions and variety, but kiwi berries consistently offer a unique combination of nutrients.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations: Kiwi Berry Nutrition Facts
While kiwi berries offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential drawbacks and considerations before incorporating them into your diet. Like any food, individual reactions can vary, and certain factors may influence their suitability for specific individuals. Understanding these potential downsides empowers you to make informed choices about your consumption.
Kiwi berries, despite their diminutive size, pack a punch in terms of nutritional value. However, this concentrated goodness can also present certain challenges for some individuals. Let’s explore some key areas to consider.
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Kiwi berries belong to the same family as kiwifruit, and cross-reactivity is a possibility. Individuals with known kiwifruit allergies should exercise caution and potentially avoid kiwi berries altogether. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin irritation (such as itching or rash) to more severe symptoms like oral allergy syndrome (itching and swelling in the mouth) or, in rare cases, anaphylaxis.
If you experience any adverse reaction after consuming kiwi berries, discontinue use and consult a medical professional immediately. Always introduce new foods gradually to monitor for any individual sensitivities.
Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
While no specific major drug interactions are widely documented for kiwi berries, their high vitamin K content warrants consideration for individuals taking anticoagulants (blood thinners) such as warfarin. Vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting, and significant fluctuations in its intake can potentially interfere with the effectiveness of these medications. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are on anticoagulant medication before making significant dietary changes, including the regular consumption of kiwi berries.
For individuals with kidney issues, the relatively high potassium content should also be monitored, as excessive potassium can be problematic for those with impaired kidney function.
Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Management, Kiwi berry nutrition facts
Kiwi berries possess a moderate glycemic index (GI), generally falling within the range of 40-50. This means they cause a relatively slow and gradual rise in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. However, the actual GI value can vary depending on factors such as ripeness and processing.
The moderate GI of kiwi berries makes them a potentially suitable choice for individuals managing blood sugar levels, particularly those with type 2 diabetes. However, portion control remains crucial. Consuming large quantities, even of moderate-GI foods, can still lead to significant blood sugar spikes. Always consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine how kiwi berries can best fit into your personalized diabetes management plan.
- Moderate Glycemic Index (GI): Generally ranging from 40-50, leading to a slower rise in blood sugar compared to high-GI foods.
- Portion Control is Key: Even moderate-GI foods can cause blood sugar spikes if consumed in excessive amounts.
- Individualized Approach: Consult a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice, especially if managing diabetes or other blood sugar-related conditions.
Essential FAQs
Are kiwi berries suitable for people with diabetes?
While kiwi berries contain natural sugars, their glycemic index is relatively low, making them a potentially suitable option for individuals managing blood sugar levels. However, moderation is key, and individuals should monitor their blood glucose levels after consumption.
Can I freeze kiwi berries?
Yes, kiwi berries freeze well. Freezing helps preserve their nutritional value and flavor. Wash and dry them thoroughly before freezing individually on a baking sheet, then transfer to a freezer bag for long-term storage.
What are the best ways to store fresh kiwi berries?
Store fresh kiwi berries in the refrigerator in a perforated plastic bag or container. This allows for proper air circulation and helps prevent spoilage. They generally last for about a week under refrigeration.


